Explain How Motion Can Be Described Using a Distance-time Graph
The y-axis shows the distance an object travels from a reference point and time is on the x-axis. If it was not constant we would see a curved line in our graph.
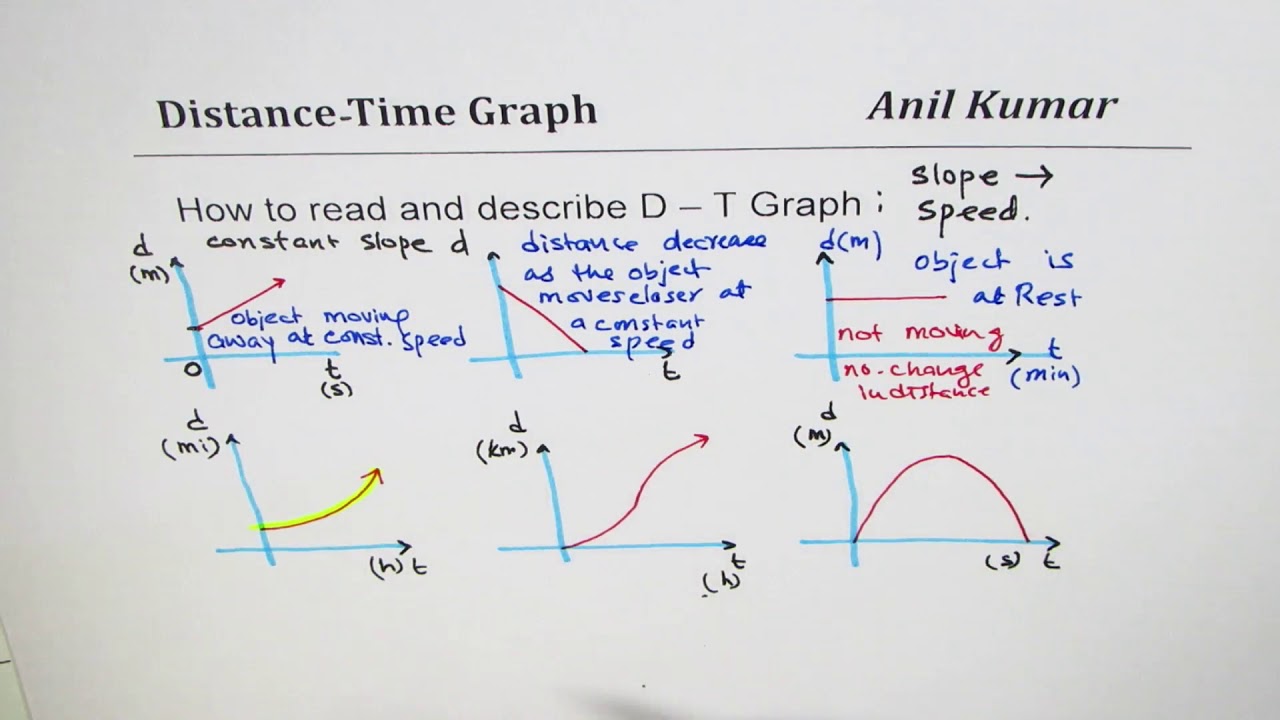
How To Read And Describe Distance Time Graph Youtube
1 question Calculate the average speed of the marble and explain how motion can be described using a distance-time graph.

. Calculate the total displacement of the object - its motion is represented by the velocity-time graph below. Here the displacement can be found by. The standard unit is the metre.
Galileo is credited as being the first to measure speed by considering the distance covered and the time it takes. Up to 24 cash back 5. If the angle of the line on a distance-time graph changes you know that the speed changes.
Distance is the total length travelled by an object. Our graph of the motion. Find average speed of Somnath to move along the rectangular path.
Motion can be described using words diagrams numerical information equations and graphs. The student assumes that as the graph goes up and down Toms path is going up and down. Describing motion with graphs involves representing how a quantity such as the objects velocity changes with respect to the time.
If an object moves along a straight line the distance travelled can be represented by a distance-time graph. The graph will have distance on the y-axis and time on the x-axis. If you are unsure about this see page page 9 of your notes and refer to the top graph of set 1.
Section Summary Motion occurs when an object changes its position relative to a reference point. Time on the horizontal axis only needs positive values. Explain how a reference point is used to give directions to a location.
Displacement is the distance and direction of a change in position from the starting point. Suggested questions and prompts. Confirmatory or Structured Inquiry Students will.
These are both used to help in the design of faster and more efficient vehicles. Δv aΔt 4ms 2 9s 36ms. It can be described using distance displacement speed velocity and acceleration.
Below you can see that the object represented by the blue line has. As you see on the graph X axis shows us time and Y axis shows position. There is a two-question quiz and a summary slide.
Graphing Motion Lesson 2-1 A graph that shows how distance and time are related is a distance-time graph. Time graphs to assess relative speed of an object. Teacher guide Interpreting Distance-Time Graphs T-3 Common issues.
Since the distance covered per unit time for the entire distance is not the same the motion is non-uniform motion. Distance is plotted on the Y-axis left and Time is plotted on the X-axis bottom. PSYW v slope riserun 20 m50 s v 4 ms v slope riserun 20 m50 s v 4 ms v slope riserun -25 m50 s v -5 ms v slope riserun -20 m50 s v -4 ms Negative slope getting flatter Negativ e slope getting steeper.
Time and velocity vs. Use the position-time graphs below to determine the velocity. Describe the motion represented by a horizontal line on a distance- time graph.
In a distance-time graph the gradient of the line is equal to the speed of the object. We observe that position is linearly increasing in positive direction with the time. The students will draw a straight line with no slope beginning at the appropriate distance.
The steeper the graph the faster the motion. 5 ways motion can be described. The motion of an object can be described in different ways.
The student assumes that a straight line on a graph means that the motion is along a straight. You use a distance-time graph to calculate _____ the average speed of an object. 4 Linear Motion Before the time of Galileo people described moving things as simply slow or fast Such descriptions were vague.
A distance-time graph shows how far an object has travelled in a given time. Plot a distance-time graph and explain whether the motion is uniform or non-uniform. A confident race car driver is cruising at a constant velocity of 20 ms.
One of the most effective methods of describing motion is to plot graphs of distance velocity and acceleration vs. From such a graphical representation it is possible to determine in what direction an object is going how fast it is moving how far it traveled and whether it is speeding up or slowing down. Up to 24 cash back Interpreting distance time graphs answer key The movement of objects can be described using motion graphs and numerical values.
Student interprets the graph as a picture For example. Start with a basic grid and draw in the x and y axes. Plugging in the acceleration 4ms 2 and the time interval 9 s we can find the change in velocity.
Up to 24 cash back A distance-time graph tells us how far an object has moved with time. Motion can also be presented graphically like the position vs. Describing Motion with Graphs Lesson 2-1.
We can see that the graph above shows a constant acceleration of 4ms 2 for a time of 9 seconds. Time graphs which show the type of motion an object undergoes in a unit of time. Students use this resource consisting of ten slides with diagrams written explanation and voice-over to understand how to plot a distance-time graph and understand what it shows.
A horizontal line means the object is not changing its position - it is not moving it is at rest. We understand from this linear increasing our velocity is constant. A downward sloping line means the object is returning to the start.
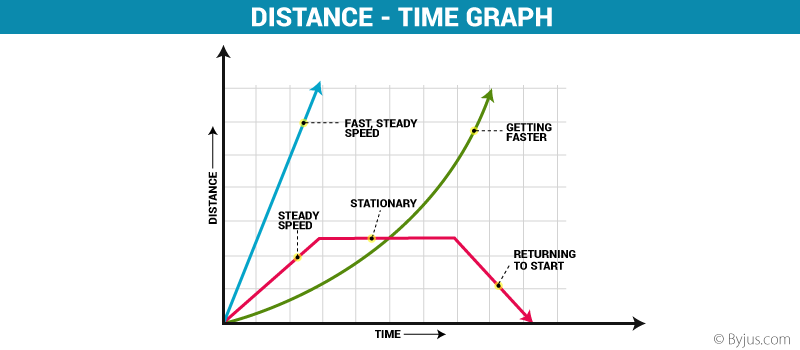
Distance Time Graph Definition And Examples With Conclusion

15 Describing Motion In A Distance Time Graph Gcsephysicsninja Com
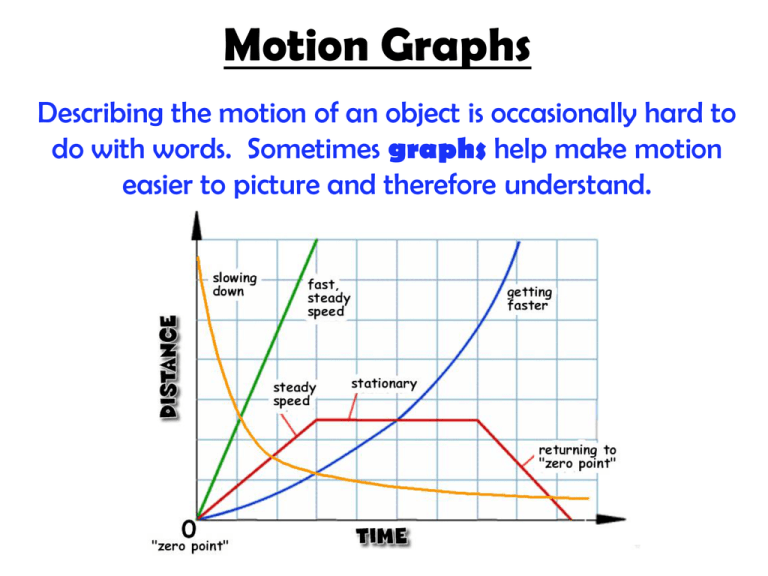
No comments for "Explain How Motion Can Be Described Using a Distance-time Graph"
Post a Comment